Introduction to EKG vs Echocardiogram:
Your heart beats around 100,000 times every day, and during each beat, it works hard to pump blood that keeps your whole body alive and healthy. But sometimes, when something starts to go wrong with this very important organ, it becomes very important to find the problem early. That’s why doctors use special tests, because catching an issue early can help you avoid big health problems and might even save your life. So, it’s also very important to understand the difference between EKG vs echocardiogram, because both of these common heart tests often work as the first tools doctors use to protect your heart and keep it working well.
While both tests evaluate your heart’s function, they work in fundamentally different ways and detect distinct types of cardiac issues. An EKG captures the electrical signals that control your heartbeat, while an echocardiogram creates detailed images of your heart’s structure using sound waves. Understanding when you might need each test, what to expect during the procedures, and how they complement each other empowers you to make informed decisions about your cardiovascular care.
This comprehensive guide will clarify the key differences between these essential diagnostic tools, helping you understand their unique roles in cardiac care. By the end, you’ll know exactly what each test reveals about your heart health and when your doctor might recommend one over the other.
What Is an EKG?
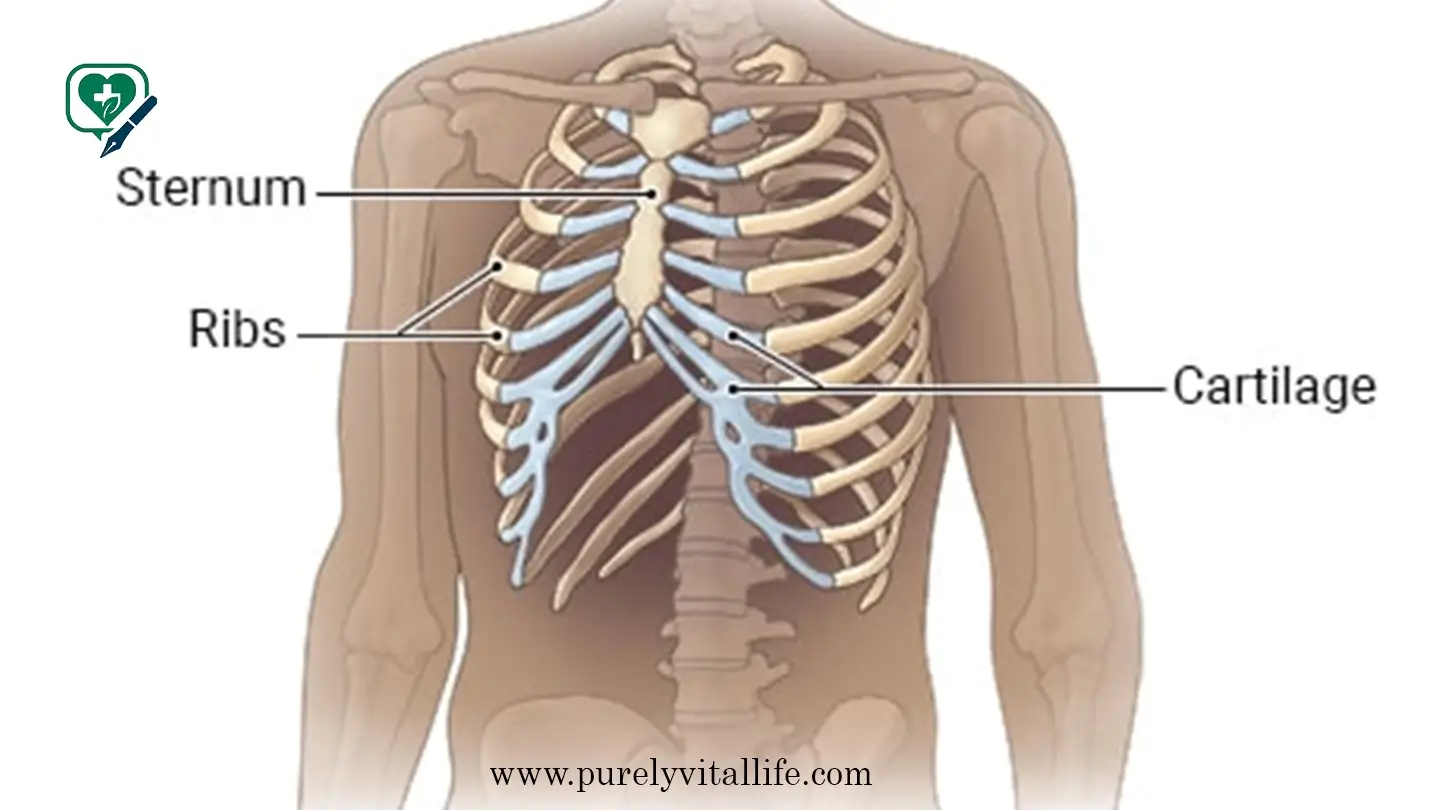
An EKG (electrocardiogram), also known as an ECG, measures the electrical activity of your heart through small electrodes placed on your chest, arms, and legs. Every heartbeat begins with an electrical impulse from your heart’s natural pacemaker, called the sinoatrial node. This electrical signal travels through your heart muscle, causing it to contract and pump blood.
The EKG machine translates these electrical signals into a visual representation—those familiar wavy lines you’ve likely seen on medical shows. Each wave and spike matches a different phase of your heartbeat, creating a detailed map of your heart’s electrical activity. When comparing an EKG vs echocardiogram, it’s important to remember that an EKG focuses on electrical signals, while an echocardiogram shows moving images of the heart’s structure.
Also Read About Is Your Morning Ritual Hurting You? The Hidden Risks of Honey & Lemon in Hot Water --- >>>
Various Heart Condistions Detects in EKG Test:
This quick, non-invasive test typically takes just 5-10 minutes to complete. Healthcare providers use EKGs to detect various heart conditions, including:
- Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
- Heart attacks, both current and previous
- Heart rate abnormalities
- Signs of coronary artery disease
- Effects of medications on heart function
- Electrolyte imbalances affecting heart rhythm
The beauty of an EKG lies in its simplicity and immediate results. Emergency room doctors often use this test as their first diagnostic tool when patients arrive with chest pain or other cardiac symptoms. The instant feedback helps medical teams make critical decisions about immediate treatment needs.
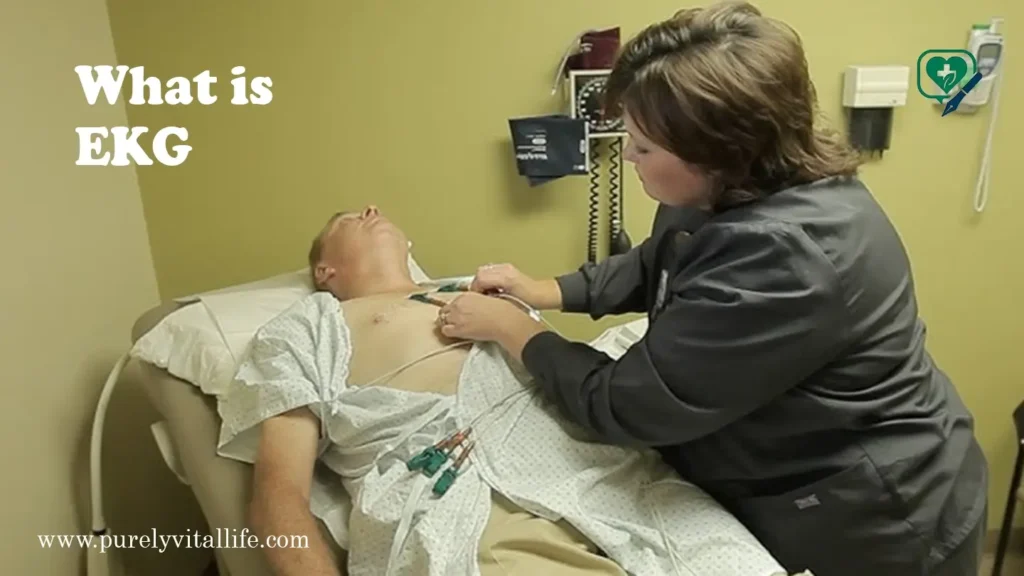
What Is an Echocardiogram?
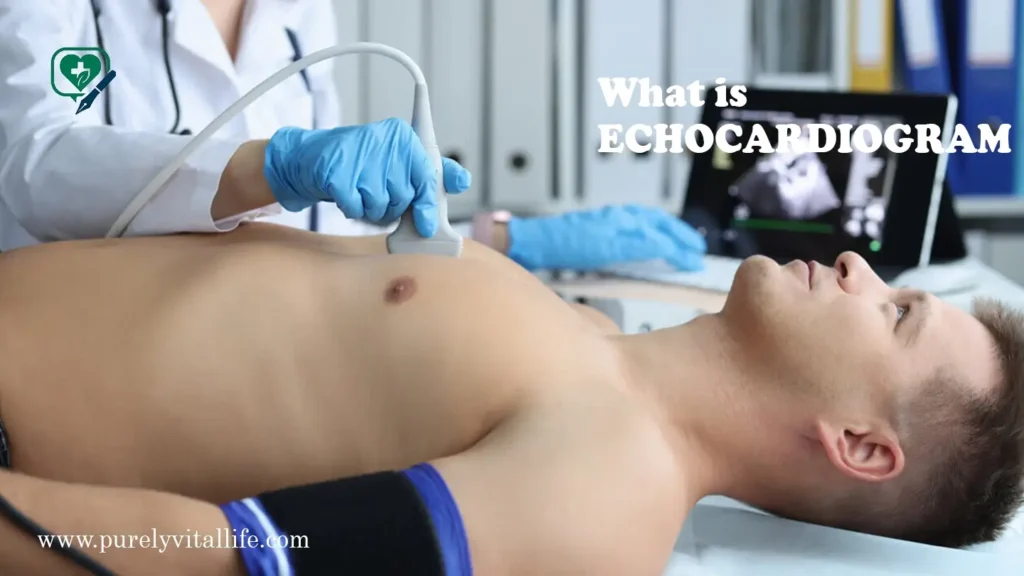
To help doctors clearly see how your heart is working, an echocardiogram uses high-frequency sound waves, also called ultrasound, and then turns them into real-time moving pictures of your heart, so they can check everything as it happens. Think of it as an ultrasound for your heart—similar to the technology used to view babies during pregnancy, but specifically designed to examine cardiac structures and function.
This sophisticated imaging test provides detailed information about your heart’s size, shape, and function. Healthcare providers can observe how well your heart chambers fill with blood, how effectively your heart muscle contracts, and whether your heart valves open and close properly.
Several types of echocardiograms serve different diagnostic purposes:
- Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE): The most common type, where a technician moves an ultrasound probe across your chest to capture images from different angles.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE): A specialized probe is gently inserted through your mouth and into your esophagus, providing clearer images of structures at the back of your heart.
- Stress Echocardiogram: Combines exercise or medication-induced stress with echocardiography to evaluate how your heart performs under physical demand.
- Doppler Echocardiogram: Uses Doppler technology to measure blood flow through your heart and blood vessels, detecting turbulence or abnormal flow patterns.
Various Heart Structure Problems Detects in EKG Test:
Echocardiograms excel at detecting structural heart problems, including:
- Heart valve diseases (stenosis or regurgitation)
- Congenital heart defects
- Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy)
- Fluid around the heart (pericardial effusion)
- Blood clots within heart chambers
- Aortic aneurysms
- Pulmonary hypertension
EKG vs Echocardiogram: Key Differences
Understanding the fundamental differences between these tests helps clarify why your doctor might recommend one over the other, or sometimes both together.
- Purpose and Function:
- EKG: Measures electrical activity and heart rhythm
- Echocardiogram: Visualizes heart structure and mechanical function
- Test Duration
- EKG: 5-10 minutes
- Echocardiogram: 30-60 minutes depending on type
- Technology Used
- EKG: Electrodes detect electrical signals
- Echocardiogram: Ultrasound waves create images
- Information Provided
- EKG: Heart rate, rhythm abnormalities, electrical conduction
- Echocardiogram: Heart size, valve function, blood flow, wall motion
- Conditions Best Detected
- EKG: Arrhythmias, heart attacks, conduction disorders
- Echocardiogram: Valve disease, structural abnormalities, heart failure
- Preparation Required
- EKG: None typically needed
- Echocardiogram: May require fasting or exercise preparation for certain types
- Cost Considerations
- EKG: Generally less expensive, often under $200
- Echocardiogram: More costly, typically $300-$2,000 depending on type and location
When Do You Need an EKG vs Echocardiogram?
Based on your symptoms, medical history, and what they find during your physical exam, your doctor will carefully look at everything and then decide which tests are best for you, so you can get the right care as soon as possible. Each test serves distinct diagnostic purposes, though they often complement each other in a comprehensive cardiac evaluation.
EEKG is typically recommended for:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeat sensations
- Dizziness or fainting episodes
- Shortness of breath
- Routine screening before surgery
- Monitoring effects of heart medications
- Following up after a heart attack
- Emergency room evaluation of cardiac symptoms
Healthcare providers often use EKGs as a first-line diagnostic tool because results are immediate and the test can quickly rule out or suggest serious conditions requiring urgent intervention.
An echocardiogram is typically recommended for:
- Heart murmurs detected during physical examination
- Suspected heart valve problems
- Shortness of breath that might indicate heart failure
- Swelling in the legs or abdomen
- Family history of inherited heart conditions
- High blood pressure that’s difficult to control
- Chest pain that might indicate structural problems
- Monitoring known heart conditions over time
When EKG vs Echocardiogram Tests Are Needed?
Many patients benefit from both tests because they provide complementary information. For example, if your EKG shows signs of a previous heart attack, your doctor might order an echocardiogram to assess how the damage affected your heart’s pumping ability. Similarly, if an echocardiogram reveals structural abnormalities, an EKG can help determine if these changes are affecting your heart’s electrical system.
Patients with complex heart conditions often require both tests for comprehensive evaluation and ongoing monitoring. Your cardiologist might use EKG results to guide the timing and type of echocardiogram needed for optimal diagnosis.
What to Expect During EKG vs Echocardiogram Test?
Understanding the testing process helps reduce anxiety and ensures you’re properly prepared for your appointment.
EKG Experience:
Preparation for an EKG is minimal. You’ll be asked to undress from the waist up and put on a hospital gown that opens in the front. First, the technician will carefully clean several spots on your skin using alcohol, because this helps the sticky pads (called electrodes) stick better and work properly.
Then, the technician will gently place small, sticky electrodes on your chest, arms, and legs. After that, the technician will connect these electrodes to wires, which then lead to the EKG machine so it can record how your heart is working. You’ll lie still on an examination table while the machine records your heart’s electrical activity for about 10 seconds to several minutes.
The procedure does not hurt at all, and most people feel completely fine during the test. However, a few people might feel a little skin irritation where the sticky pads were placed. Still, once the test is done, you can get up right away and go back to your normal activities without waiting or resting.
Read More About Feeling Dizzy After Eating? Understand the Causes and Find Relief — >>>
Echocardiogram Experience:
Echocardiogram preparation varies depending on the type of test ordered. Usually, you don’t need to do anything special to get ready for a standard transthoracic echocardiogram. First, the nurse or technician will ask you to take off your clothes from the waist up. Then, you will lie down on your left side on a soft examination table, which helps them see your heart better.
The technician will apply a clear gel to your chest and use a transducer (ultrasound probe) to capture images from different positions. During the test, the technician might ask you to move into different positions so they can see your heart more clearly. Also, you may be asked to hold your breath for a few seconds or breathe in a special way, because these actions help make the heart images clearer.
The whole test does not hurt, so you won’t feel any pain. However, some people do notice that the gel feels cold when it’s put on their chest. Also, when the technician presses the device (called a transducer) against your skin, a few people feel a little uncomfortable from the pressure—but not everyone feels that way. The room is often darkened to help the technician see the images clearly on the monitor.
For specialized echocardiograms:
- TEE: Requires fasting for 4-6 hours beforehand and mild sedation during the procedure
- Stress Echo: May involve exercise on a treadmill or medication to simulate physical stress
- Contrast Echo: Might require an IV line for contrast agent injection
FAQs About EKG Vs Echocardiogram:
- How long does an echocardiogram take?
- Answer: A standard transthoracic echocardiogram typically takes 30-60 minutes. More specialized types like TEE or stress echocardiograms may take 60-90 minutes, including preparation time.
- Is there any difference between EKG and ECG?
- Answer: No, EKG and ECG refer to the same test. Doctors use both “EKG” and “ECG” to talk about the same heart test. First, the word “EKG” comes from the German word “elektrokardiogramm.” Meanwhile, “ECG” is the English short form of the word “electrocardiogram.” Even though they look different, both terms mean the same test that checks how your heart is working. Both terms are used interchangeably in medical settings.
- Does insurance cover these tests?
- Answer: Most insurance plans cover both EKG vs echocardiogram when medically necessary and ordered by your physician. Coverage details vary by plan, so check with your insurance provider about specific requirements or copays.
- How often should I have these tests?
- Answer: The frequency depends on your health status and risk factors. People with known heart conditions might need regular monitoring, while healthy individuals might only need these tests when symptoms develop or as part of routine screening based on age and risk factors.
- Can these tests detect all heart problems?
- Answer: While EKG vs echocardiogram are powerful diagnostic tools, they can’t detect every type of heart problem. Some conditions require additional tests like cardiac catheterization, CT scans, or MRI for complete evaluation.
Taking Charge of Your Heart Health:
Both EKG Vs echocardiogram serve crucial roles in maintaining and monitoring your cardiovascular health. These tests work together to provide a comprehensive picture of how your heart functions, from its electrical system to its physical structure and pumping ability.
The key difference lies in their focus: EKGs excel at detecting rhythm problems and electrical abnormalities, while echocardiograms reveal structural issues and mechanical function. Neither test is superior to the other—they’re complementary tools that together help your healthcare team make informed decisions about your cardiac care.
Don’t wait for symptoms to become severe before seeking evaluation. If you’re experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, or other concerning symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider promptly. Early detection through appropriate testing can prevent minor issues from becoming major health problems.
Ready to take the next step in understanding your heart health? Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss whether cardiac testing might benefit you. Your heart works tirelessly for you every day—isn’t it worth giving it the attention and care it deserves?