
Introduction to Genetic Mutations:
Genetic mutations are changes to our DNA that can drastically change how our bodies operate, from cancerous tumors or hereditary disorders to more subtle effects like no noticeable impact or even possible benefits. At Purely Vital Life, we help you explore this fascinating world of mutations – their causes, impacts, and how they may impact on health and wellbeing.
In this article, you’ll gain an understanding of genetic mutations and their different forms. Furthermore, learn why early genetic screening and lifestyle choices are critical in managing genetic risks effectively.
What are Genetic Mutations:
Genetic mutations are changes or alterations to the DNA sequence that constitutes a gene. Our bodies depend on this genetic code for producing proteins, which carry out most functions within cells. Even minor modifications could disrupt its performance or stop working altogether.
Our parents pass some mutations to us. We inherit these as germline mutations. Environmental factors cause other mutations during life. Cells make errors while copying DNA, which creates somatic mutations. These mutations affect how our body works. Either inherited or acquired, these mutations may increase our risk for certain diseases or conditions, including various types of leukemia, which often result from somatic genetic changes in blood-forming cells.

Types of Genetic Mutations:
Genetic mutations change our DNA in specific ways. Each mutation affects the body differently. Doctors study these changes to understand their effects. They identify harmful mutations and link them to diseases. By becoming acquainted with them all it helps identify which one could pose the biggest health threat.
Point Mutations:
Point mutations involve changing one DNA base pair. This small change may alter a protein’s function or stability; sometimes this effect is minor but in other instances point mutations can cause serious genetic conditions like sickle cell anemia.
Deletions:
Deletion mutations remove parts of our DNA. These deletions destroy important genetic instructions. Cells fail to make proper proteins. The body suffers because the proteins don’t work correctly. Some forms of muscular dystrophy such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy result from deletion mutations.
Insertions:
Insertion mutations add extra DNA into the gene. These insertions confuse the cell’s reading process. Cells build faulty or broken proteins. These proteins disrupt normal body functions. Insertion mutations are common in many genetic disorders and cancers.
Duplications (aka Gene Duplications):
DNA duplication results in copying portions more than once, leading to overproduction of proteins or interfering with normal development; for instance, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease has been associated with gene duplications.
Frameshift Mutations:
Frameshift mutations occur when there is an alteration to DNA reading frame due to deletion or insertion, altering protein structure in ways that often render it inactive – this type of mutation being one of the most dangerous types.
Chromosomal Mutations:
These mutations affect entire sections of chromosomes rather than individual genes; Down Syndrome and Turner syndrome are caused by these types of mutations.
Also Read About Top Hepatitis A Specialists: When and Why You Should See One — >>>
Causes of Genetic Mutations:
Genetic mutations may result from either internal biological processes or external environmental influences, or both.
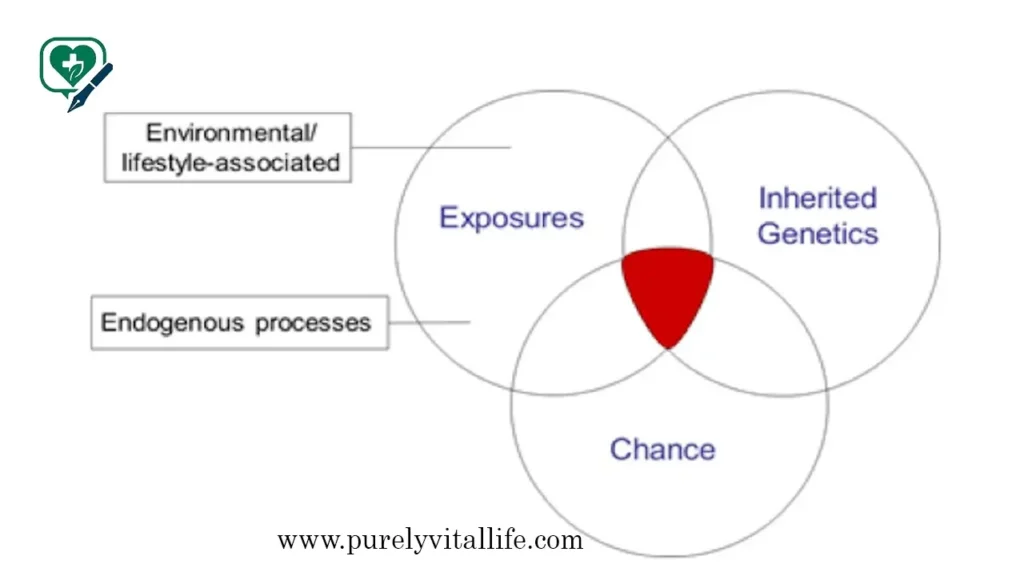
Inherited Mutations:
You can inherit mutations from both parents during reproduction. Mutations affects every cell in your body and can be passed down from generation to generation.
Environmental Factors:
Radiation, chemicals (like benzene or asbestos), and pollutants such as PM2.5 have all been linked to DNA mutation. Intense sun exposure and smoking are other potential environmental sources.
Errors during DNA Replication:
Each time a cell divides, its DNA must be copied accurately; occasionally this process leads to errors; although our bodies have mechanisms in place to correct for them, some slip through and become permanent mutations.
Viral Infections:
Certain viruses such as HPV (human papillomavirus) have the ability to integrate their genetic material into human DNA and lead to mutations that result in cancerous tumors.
How Genetic Mutations Affect Your Health:
Genetic Disorders:
An inheritance of mutations may cause serious genetic diseases like cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease and Huntington’s disease which are all caused by specific mutations that have been passed down from generation to generation.
Increased Risk of Cancer:
Cancer often develops from genetic mutations that cause cells to proliferate uncontrollably; mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 increase your risk significantly of breast and ovarian cancer.
Immune System Disorders:
Mutations can also alter the ability of your immune system to function optimally; mutations in certain genes can even result in primary immunodeficiency diseases.
Neurological Conditions:
Genetic mutations may disrupt brain function and development, leading to diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or epilepsy.
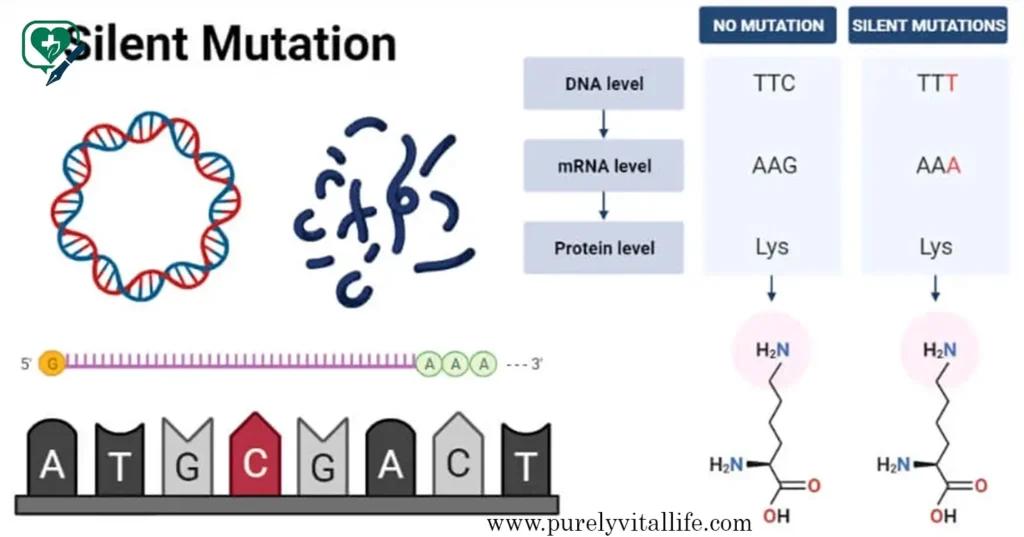
Silent Mutations:
Not all mutations cause issues; some may remain silent, meaning they don’t alter how the body functions and can even be passed down from parent to child without presenting any health concerns. These mutations tend to be harmless but could potentially pass onto future generations as inheritance.
Detection and Importance of Genetic Testing:
Genetic Testing to Identify Mutations Genetic testing plays an integral part in early identification of genetic mutations. It involves analyzing someone’s DNA to detect changes that could potentially cause disease or impact treatment decisions.
- Doctors may recommend genetic testing in order to:
- People with genetic diseases in their families should seek genetic testing as soon as possible.
- Couples planning to have children are typically expected to start planning prior to conception.
- Assist cancer patients in treatment planning.
Individuals experiencing mysterious health conditions could benefit from seeking help for any further explanations.
Early diagnosis through testing helps facilitate more effective prevention, tailored treatment plans and informed health decisions.

Can You Prevent Genetic Mutations?
Unfortunately, while inherited mutations cannot be prevented, somatic mutations may be reduced through healthy lifestyle choices that reduce your risk.
- Avoid smoking and excessive drinking
- Use sunscreen to safeguard against UV radiation.
- Protect against environmental toxins
- Eat a diet rich in antioxidants.
- Stay physically active and manage stress effectively by remaining physically active and managing it effectively.
These habits can help keep your cells healthier over time and help reduce DNA damage.
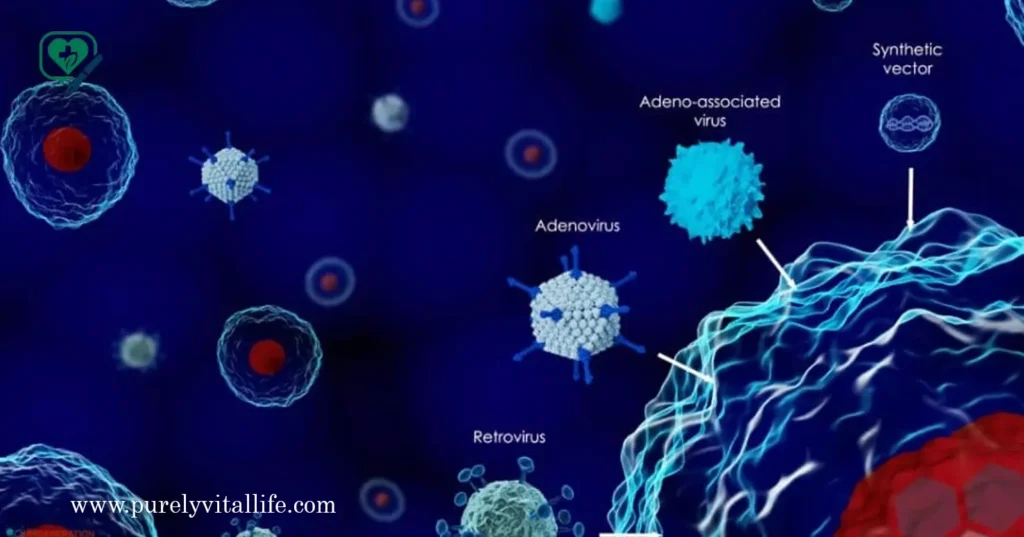
Gene Therapy as a Future Solution:
Gene therapy is an exciting medical advancement aimed at correcting defective genes responsible for disease. Scientists are developing techniques to accomplish this aim.
- Substitute mutant genes with healthy ones
- Switch off dysfunctioning genes
- Introduce new genes to help fight disease.
Although still in its infancy for many conditions, gene therapy has shown promise in treating rare genetic disorders and cancers.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Genetic Mutations Is Essential
An in-depth knowledge of genetic mutations is integral for making informed health decisions. While not all mutations may have devastating health ramifications, certain can have profound life-altering repercussions that should not be ignored. Thanks to recent scientific developments we now have better tools available to detect, monitor and potentially correct some mutations.
At Purely Vital Life, our mission is to equip you with accurate and useful health information so you can stay informed and take proactive measures to safeguard both your own wellbeing as well as that of those close to you.






Very insightful piece. The explanation of how genetic mutations affect health is easy to understand and highlights why DNA plays such a vital role.