Introduction to Oral Cancer Stages:
Oral cancer is a devastating disease affecting the mouth, lips, tongue and throat. Understanding oral cancer stages is crucial to early detection, prompt treatment and increased survival rates. At Purely Vital Life we aim to provide clear insight into its progression as well as symptoms to look out for and the treatments available at each stage.
What Is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer refers to any malignant growth found within the oral cavity or surrounding tissues, affecting lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, floor of the mouth and even throat tissues. Early detection increases treatment success while decreasing complications; risk factors include tobacco use, alcohol intake, human papillomavirus (HPV) infections and prolonged sun exposure to lips.
Understanding Oral Cancer Stages Is Essential:
Understanding the stages of oral cancer helps both patients and healthcare providers alike:
- Early Detection: Spotting cancer early can result in less invasive treatments and treatments may require less medication.
- Treatment Planning: Physicians can recommend the most appropriate therapy according to the stage and grade of cancer.
- Prognosis: At each stage, outcomes and survival rates become clear.
Also Read About EKG vs Echocardiogram: Understanding Heart Tests That Save Lives — >>>
EKG vs Echocardiogram: Understanding Heart Tests That Save Lives
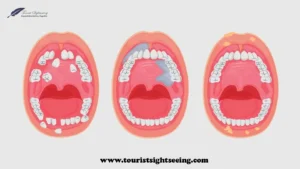
Oral Cancer Stages Provide An Overview:
Oral cancer can typically be divided into four stages, each representing its progression and spread.
Carcinoma in Situ) at this stage:
Stage 0 represents the initial phase of oral cancer, commonly referred to as carcinoma in situ. At this stage:
- Cancerous cells may exist but have yet to reach deeper tissues.
- Symptoms may be minimal or absent, often appearing as white or red patches in the mouth.
- Treatment typically includes surgical removal of abnormal cells.
Early diagnosis at Stage 0 offers the highest likelihood of successful treatment.
Stage I:
Its initial stage – At Stage I, oral cancer is usually small and localized:
- Tumor size typically falls within 2 cm.
- Cancer has not spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
- Symptoms may include persistent mouth sores, mild pain or changes to oral tissues.
- Treatment options may include surgery followed by radiation therapy to help prevent future recurrences.
Patients diagnosed at Stage I typically enjoy an optimistic prognosis.
Stage II oral cancer signifies:
stage II oral cancer indicates:
- Tumor Size between 2 cm to 4 cm.
- Cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Symptoms may include difficulty eating or swallowing, persistent pain or swelling.
- Treatment typically includes surgical removal of the tumor combined with radiation therapy.
Early intervention can prevent further spread and complications in Stage II.
Stage III oral cancer progresses more significantly:
Tumor size exceeds 4 cm or has spread to one lymph node on one side of the neck.
- As time progresses, symptoms worsen; this includes persistent mouth pain, bleeding and difficulty speaking or swallowing.
- Treatment often includes surgery, radiation and/or chemotherapy as an integrated package.
- Stage III requires active monitoring and treatments designed to achieve positive outcomes.
Stage IV Oral Cancer:
This stage represents the most advanced form of oral cancer:
- Cancerous tumors have metastasized to multiple lymph nodes or distant organs (metastasis).
- Symptoms are severe and include persistent pain, difficulty eating, significant weight loss and facial swelling.
- Treatment should be aggressive and may involve surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy or targeted therapy.
Early detection is crucial as Stage IV cancer carries a lower survival rate compared to earlier stages.
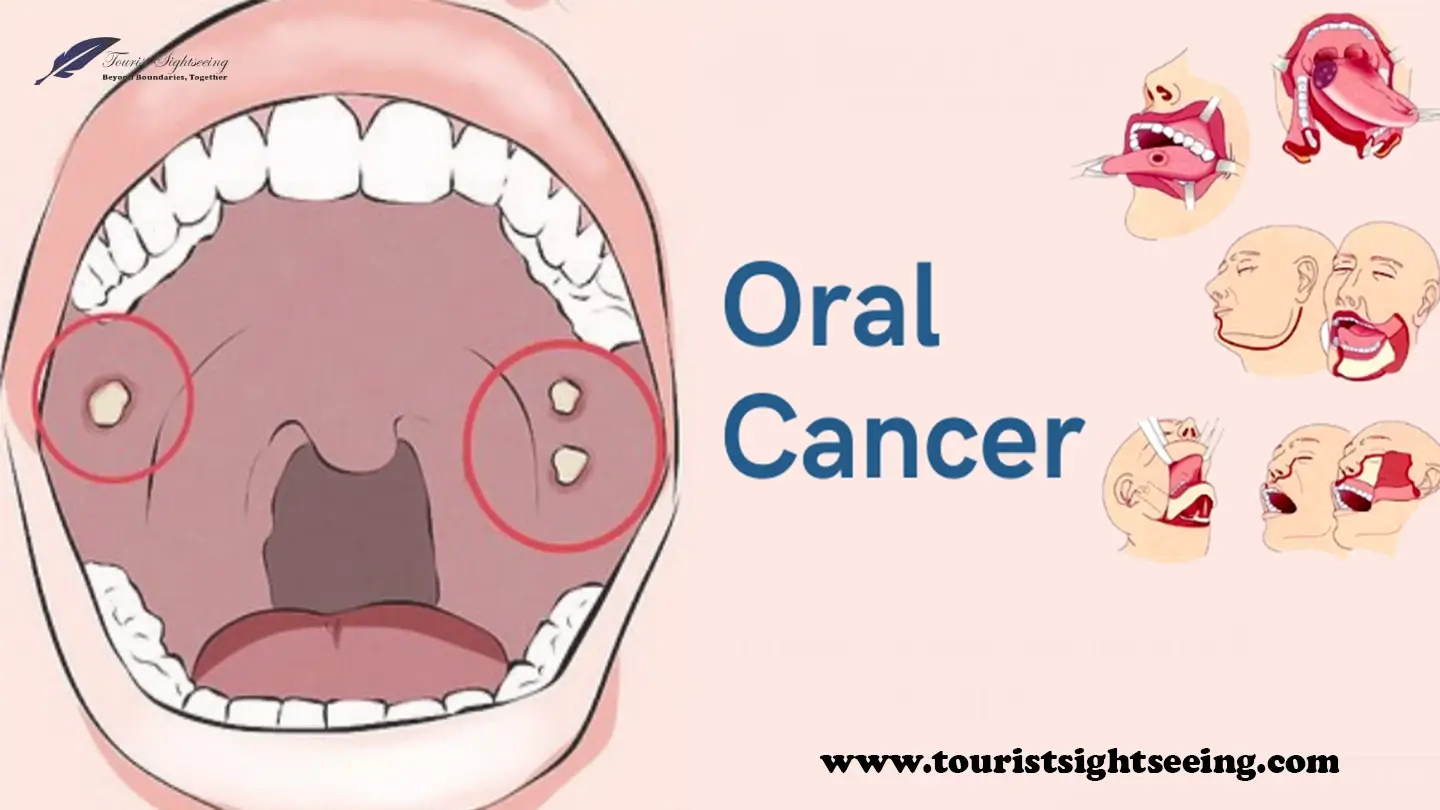
Common Symptoms in All Stages:
Signs of oral cancer to watch out for may differ depending on individual cases, however these indicators include:
- Persistent mouth sores or ulcers have become a serious health concern in recent months, prompting repeated visits to dentists for care.
- White or red patches in the mouth
- Sufferers of discomfort or difficulty swallowing have difficulty with swallowing.
- Numbness or swelling in the face or mouth
- Issues such as loose teeth or dentures no longer fitting properly
If any of these symptoms last more than two weeks, seeking medical advice is highly advised.
Diagnosing Oral Cancer Stages:
Doctors use various means to assess the stage of oral cancer:
- Biopsy: Removing tissue samples for laboratory analysis.
- Imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, PET scans or X-rays may be performed to accurately gauge tumor size and spread.
- Endoscopy: Visual examination of the throat and oral cavity using endoscope.
Accurate staging ensures patients receive the most beneficial treatment plan.
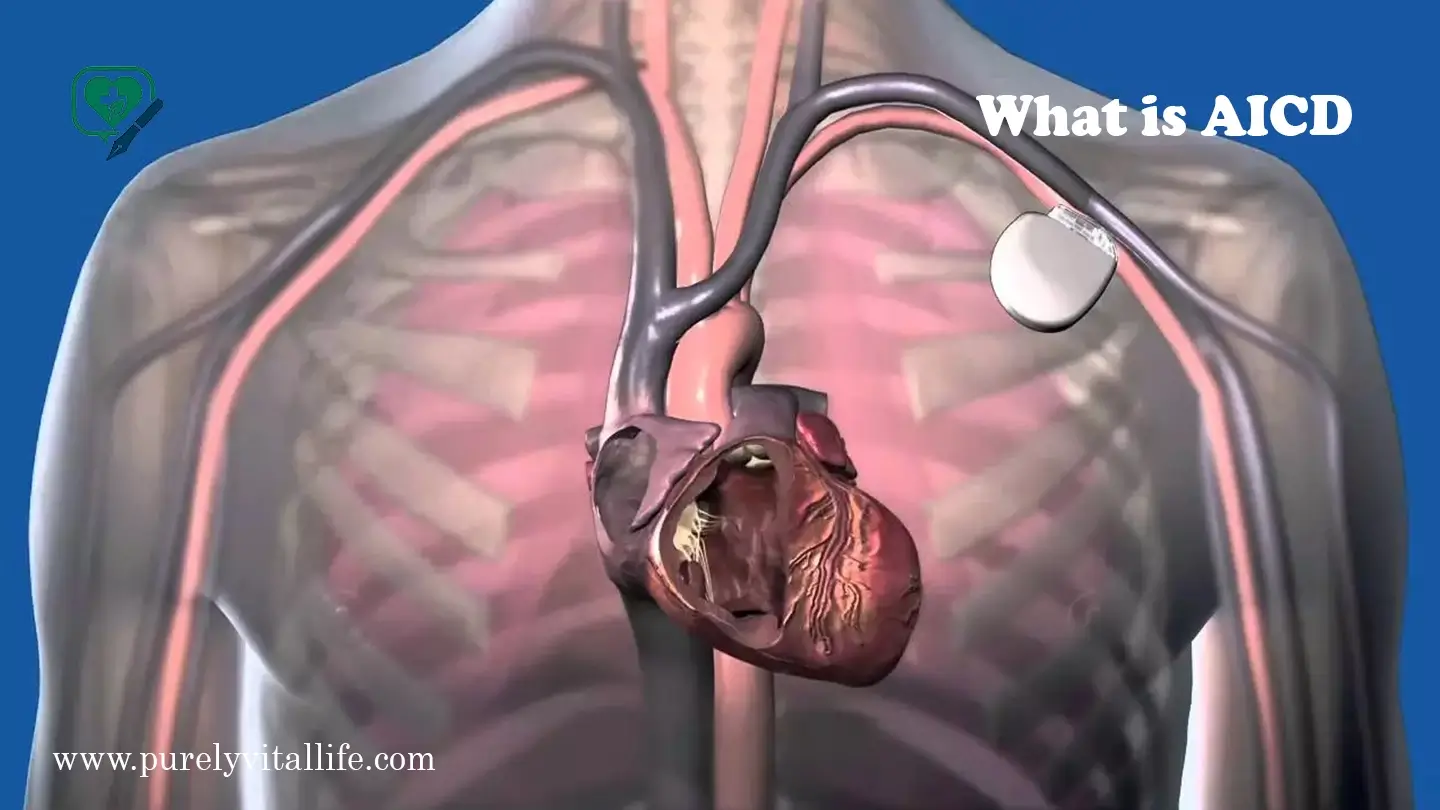
AICD Medical Abbreviation Explained: Meaning, Uses, and Importance in Cardiology
Based on Stages of Treatment:
Treatment options for oral cancer depend on its stage and location:
- Surgery: Removal of tumors and, in certain instances, surrounding lymph nodes.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy rays target cancer cells, often used after surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs used to destroy cancerous cells, typically for more advanced cases.
- Targeted therapy: Medication that specifically targets cancer cell mechanisms.
Early-stage cancer typically requires less aggressive therapies, while later stages may necessitate combination therapy approaches.
Preventive Measures and Early Detection are Crucial:
Preventing or early diagnosing oral cancer can significantly enhance outcomes; early detection offers better chances for survival and success outcomes:
- Avoid tobacco and limit alcohol intake.
- Maintain a high standard of oral health through regular dental check-ups and care.
- Prevent lips from experiencing excessive sun exposure by protecting them with sunblock.
- Maintain a close watch for any changes in the mouth, such as sores or discoloration.
At Purely Vital Life, we recognize the value of early detection as being essential to saving lives.
Conclusion:
An understanding of oral cancer stages is integral for early diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved prognosis. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking healthcare immediately are proven ways of increasing chances of recovery; additional factors that help include regular dental check-ups, healthy lifestyle choices and being aware of risk factors as means of prevention.
Early intervention and knowledge of stages can make all the difference in terms of outcome. At Purely Vital Life, we urge readers to prioritize oral health by staying aware of possible oral cancer risks.